A surgical skills assessment rubric for pterygium surgery
Purpose To introduce an assessment tool (rubric) for evaluating ophthalmology residents’ competency in pterygium surgery. Methods A panel of experienced international surgeons collaborated and developed the rubric. After describing various stages of the procedure, the Dreyfus scale of skill acquisition was used for scoring each stage. After finalizing the rubric, two surgeons independently evaluated 20 masked pterygium surgery videos of 10 residents and scored the videos according to the rubric. The agreement between the scores of them was examined with the intra-class correlation coefficient test. Results This rubric divides pterygium surgery into 13 different stages and covers the two most common techniques of pterygium surgery; conjunctival autograft and amniotic membrane transplant. The rubric showed face and content validity. Overall, an intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.90 (95% confidence interval 0.76–0.96, P < 0.001) was achieved between the two surgeons. The residents scored significantly ...
A rare combination of late-onset post-LASIK keratectasia after early-onset central toxic keratopathy
We have presented the clinical findings of a case with bilateral early-onset central toxic keratopathy (CTK) followed by bilateral late-onset post-LASIK keratectasia. Laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) is a safe procedure to treat a broad spectrum of refractive errors; however, unexpected and rarely encountered post-LASIK complications could be a challenge for patient and surgeon. Post-LASIK keratectasia is a significant consequence of the LASIK operation that may appear anywhere from one week to many years after the procedure[1]. Although the exact incidence rate of post-LASIK keratectasia remains debatable, it was estimated to be from 0.04 to 0.6%[1]. Post-LASIK keratectasia causes progressive corneal thinning, central/paracentral corneal steepening, irregular astigmatism, and reduced the best distance corrected and uncorrected visual acuity (CDVA and UDVA)....
A joinpoint and age-period-cohort analysis of ocular cancer secular trends in Iran from 2004 to 2016
Investigating secular trends of ocular cancer registration in Iran. After acquiring Iranian national population-based cancer registry data, trends of age-standardised incidence rates (ASIR) of ocular cancers and annual percent changes (APC) between 2004 and 2016 were analysed in age groups, gender, topography and morphology types with joinpoint regression analysis. Age, period, and cohort effects on incidence rates were estimated by age-period-cohort model. Geographic distribution of ASIR was assessed using GIS. Overall ASIR of ocular cancers was 16.04/100,000 (95% CI 15.77-16.32). Joinpoint regression analysis showed a significant increase of ASIR between 2004 and 2009 for males (APC = 5.5, 95% CI 0.9-10.2), ages over 50 years (APC = 5.2, 1.2-9.4), skin/canthus/adnexal cancers (APC = 4.2, 0.8-7.7), and carcinomas/adenocarcinomas (APC = 4.3, 0.6-8.1); however, between 2009 and 2016 a declining trend was observed in all investigated variables....
A criticism on the article History of Bacterial Infection Diseases in Iran
In issue 4 of the Iranian Journal of Medical Microbiology (Volume 12, Issue 4, 2018, pp.230-238), an article entitled “History of Bacterial Infection Diseases in Iran" was published by Akbar Mirsalehian and Mosayeb Dalvand (http://dx.doi.org/10.30699/ijmm.12.4.230). Respected authors of the article with the aim of re-reading the history of common bacterial infectious diseases in Iran in a part of the study examined the history of trachoma infectious disease. Despite some important therapeutic measures in the fight against trachoma, but historical sources and documents show that important aspects of trachoma have not been carefully considered by researchers. Owing to the importance of medical history studies in medical research, please publish the following points in one of the journal's issues as a letter to the editor.
A Comparison of Lower Eyelid Retraction in Normal Individuals with Positive versus Negative Orbital Vector
The present study aimed to compare lower eyelid retraction (LER) in individuals with a positive orbital vector with that of individuals with a negative orbital vector. MATERIALS AND METHODS: This cross-sectional study was conducted on 123 normal individuals including 64 men and 59 women aged 20–80 years. After the individuals underwent Hertel exophthalmometry, two side-view and front-view photos were taken using a camera. The orbital vector angle and the extent of scleral show were then measured in millimeter, using the Photoshop software. Eventually, the recorded data were analyzed through statistical software. RESULTS: The findings of this study showed that LER has a significant correlation with orbital vector angle and the extent of proptosis (P < 0.05). The mean value of orbital vector angle in individuals without LER was 9.76°, while this figure was calculated to be − 13.65° in individuals with LER. The mean protrusion value based on Hertel exophthalmometry was 14.08 mm in individuals without LER...
A Review of Monkeypox Ocular Manifestations and Complications: Insights for the 2022 Outbreak
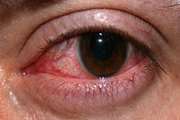
Monkeypox (MPVX) infection has been associated with multiorgan presentations. Thus, monkeypox infection’s early and late complications are of particular concern, prompting health systems to decipher threatening sequels and their possible countermeasures. The current article will review the clinical signs and symptoms of the present and former outbreaks, differential diagnoses, workup and treatment of the ocular manifestations of MPXV infection in detail. One of the uncommon yet considerable MPXV complications is ocular involvement. These injuries are classified as (1) more frequent and benign lesions and (2) less common and vision-threatening sequels. Conjunctivitis, blepharitis and photophobia are the most uncomplicated reported presentations. Moreover, MPXV can manifest as eye redness, frontal headache, orbital and peri-ocular rashes, lacrimation and ocular discharge, subconjunctival nodules and, less frequently, as keratitis, corneal ulceration, opacification, perforation and blindness.

.jpg)


.jpg)

_1_crop.png)