The microenvironment of ocular surface in keratoconus a systematic review
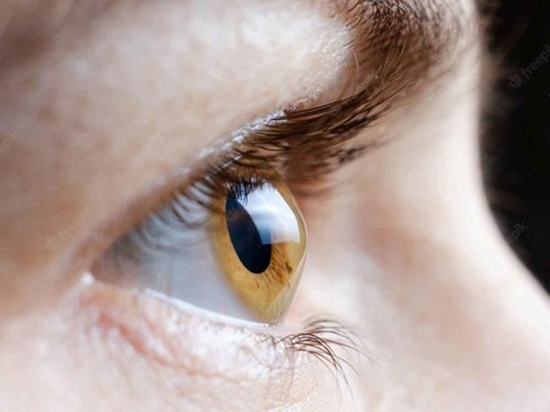
Keratoconus is a progressive corneal ectatic disorder characterized by thinning and irregularity of the cornea, significantly impairing visual acuity. Recent studies have explored how non-ectatic conditions, such as dry eye and tear film instability and alteration of the ocular surface microenvironment, contribute to the development and progression of keratoconus. This comprehensive review aims to investigate the complex relationship between keratoconus and ocular surface diseases by examining the microenvironmental changes that occur on the ocular surface throughout the course of keratoconus, as well as the related clinical implications.
In this PROSPERO-registered study (ID: CRD42025643808), PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane, Embase, Web of Science, and Google Scholar were thoroughly searched to retrieve all pertinent papers published up to January 2025. The retrieved publications were then reviewed, and the eligible ones were included.
Keratoconus, with a similar inflammatory profile to that of ocular surface disease, has elevated Interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9, contributing to extracellular matrix degradation and stromal thinning. Tear film instability, altered lipid secretion, and oxidative stress exacerbate disease progression. These findings suggest that keratoconus is not only a biomechanical disorder but also an inflammation-driven one.


_1_crop.png)
Leave a comment